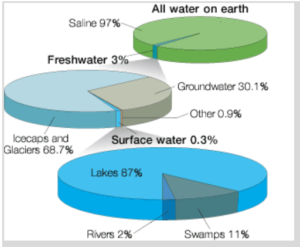
Earth has been referred to as the “Water Planet” by NASA, being about 70% of it covered with water. According to the US Geological Survey, however, only about 3% of it is freshwater. And only about 0.3% of this freshwater is easily accessible surface water i.e., lakes, rivers, etc. The image below attempts to visualize how small the quantity of freshwater is, that is available for our safe consumption. This surprising realization brings with it a great responsibility on us human beings regarding the dutiful and sustainable use of this valuable resource.
Water Scarcity
Being the key driver of life on earth, water is integrated with and affects many other aspects of life i.e., food supply chains, global economies, energy, and inter-state relations.
Unfortunately, despite being the single most valuable natural resource, it is being misused on both global and local levels, to an alarming degree. So much so that the present generation is going through a global freshwater shortage crisis. A report published in Frontiers, a science journal, attempts to put the water scarcity issue into perspective. The report claims that presently, about 40% of the world’s population is experiencing water scarcity. The major cause of this issue is mainly attributed to the continuously increasing global population, widespread industrialization, and urbanization of the human population, to name just a few among the plethora of other factors.
The issue of water scarcity has worsened even further as a result of the water pollution our industries are causing. Industries discharge their wastewater, highly contaminated with organic pollutants, heavy metals, nutrients, and other toxic products, into open freshwater bodies. The introduction of these contaminants results in oxygen depletion and eutrophication. Such an aquatic environment leads to the death of flora and fauna and makes the water unfit for human consumption.
Approaches to enhance the water value chain
But, fortunately, not everything is lost. Although water scarcity is referred to as a global crisis, it is through collective effort and innovative solutions that we can still hope for a sustainable future. Below mentioned are some key things that we can adopt to pave the path towards a water-secure world.
- Water conservation training and education
Water conservation happens on multiple levels within the domestic ecosystem. At level one we need to educate individuals, communities and students, regarding the responsible use of water. This can be done in schools by educating kids regarding water consumption and encouraging sustainable water consumption behaviors and by displaying sign boards, at public water distribution units, prompting citizens to use water responsibly.
- Water efficient utilities
Introducing water-efficient utilities i.e., water-efficient faucets, showers and rainwater harvesting in our homes and offices to reduce water consumption and promote the culture of recycling.
- Individual domestic wastewater treatment technologies
Several potential small-scale water treatment options are currently available for use. SODIS, short for Solar Distillation, and Life-straw filter are prime examples of such small-scale options.
Although efficient in their treatment these small innovative options do not promise complete removal of all the contaminants that are usually present in domestic wastewater. Apart from that they are only restricted, at best, to only individual users and are not scalable.
Domestic treatment Options for European countries
Innovative technologies are emerging that promise compact treatment units that aim to reduce the drawbacks of conventional approaches and have very minimal energy requirements that render the wastewater recyclable.
BioTornado has developed iconic products that aim specifically at the treatment of domestic wastewater and commercial buildings. The unit hence fabricated is compact, user-friendly, easily installed, and made from recycled plastics which fits seamlessly into an already-built domestic environment. The unit is designed with very few moving parts and advanced technology that ensures low and easy maintenance.
Fluence has developed a Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR), an ingenious amalgam of membrane technology with conventional wastewater treatment. The technology aims at reducing energy demand linked with aeration requirements for the activated sludge.
Ecolab offers sustainability Solutions in the domain of water, hygiene and infection prevention solutions and services that protect people and the resources vital to life.
While deciding to install domestic wastewater one should not only look at the upfront cost of domestic wastewater installation but also look into durability energy, maintenance Cost and effluent quality.
Although the capital investment associated with the installation of domestic wastewater units is handsome, the energy savings, low maintenance and automated operations, and reduction in water bills as a result of recycling treated wastewater makes the investment quite a lucrative deal.